Microservices architecture
Microservice is an architectural style of developing software systems; that structures an application as a collection of smaller independent services. These services exist independently as well-defined interfaces, highly maintainable and Loosely connected via APIs.
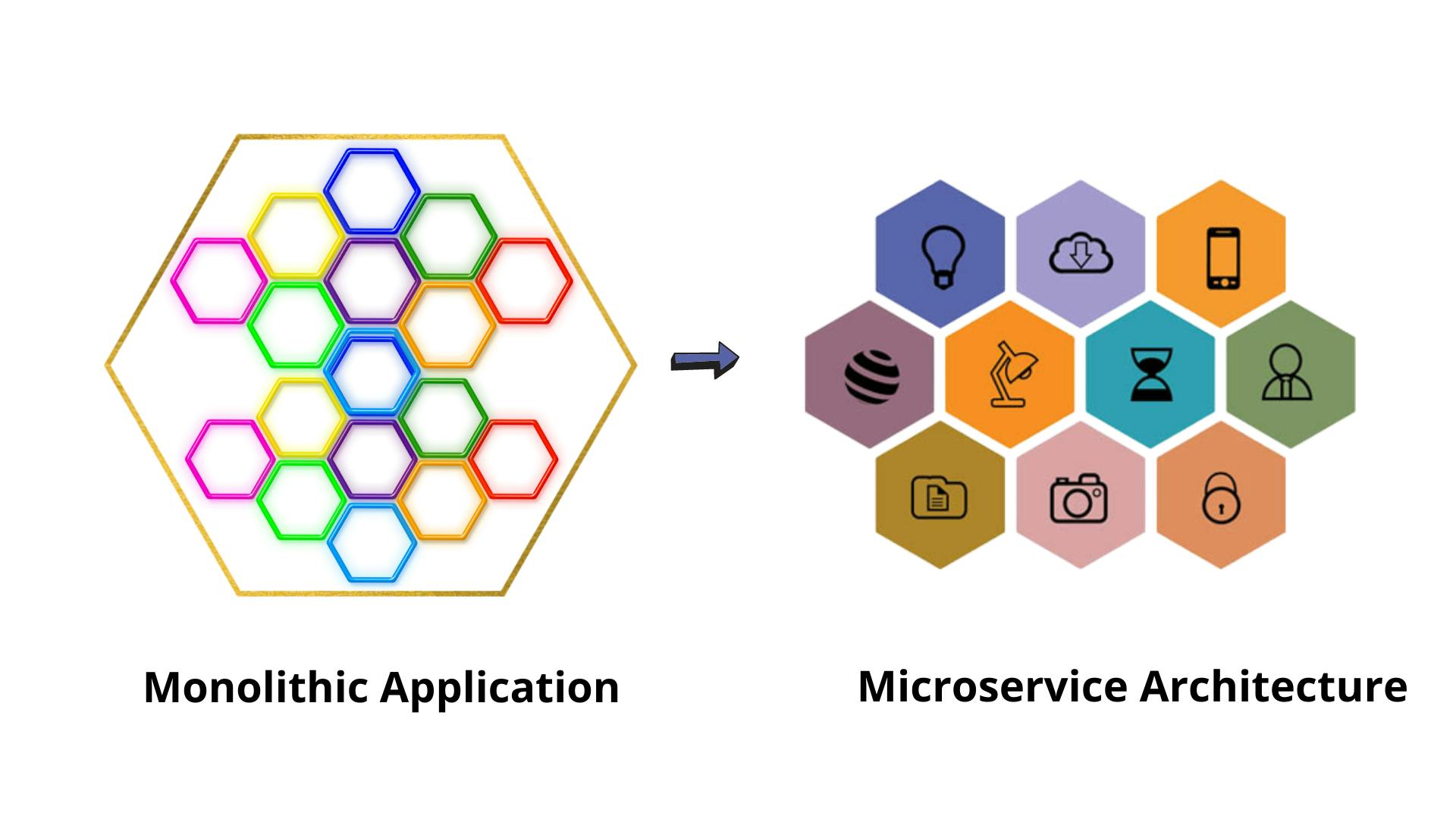
Backstory
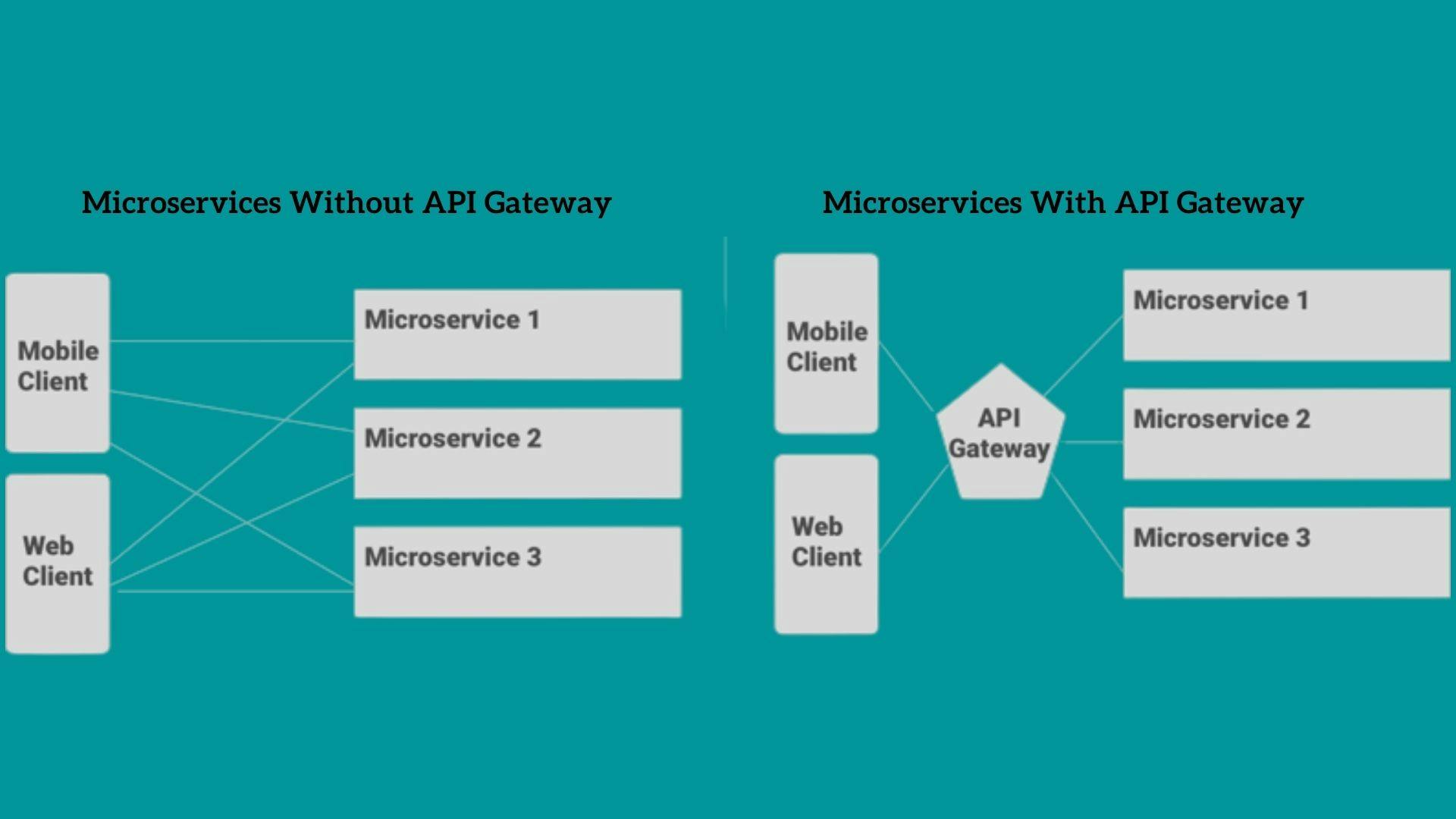
After the monolithic era, most big monolithic applications were divided into independent subsets called microservices. These microservices were scalable, secure and agile. However, managing the communication between these multiple microservices became tricky. Clients had to keep track of each microservice and its address, which became complex. This brought about the demand for a mid-layer service like API gateways (e.g., APISIX); that provide authenticating, monitoring, load balancing, caching, request shaping, and managing client and microservice interactions.
What Is An API Gateway?
API gateway is an infrastructure layer between the client apps and the microservices. Its purpose is to act as a proxy, and it receives requests from different clients. Then process to send API calls to specific internal services based on characteristics in clients requests. It further aggregates the results obtained from the microservices and sends them back to the client.
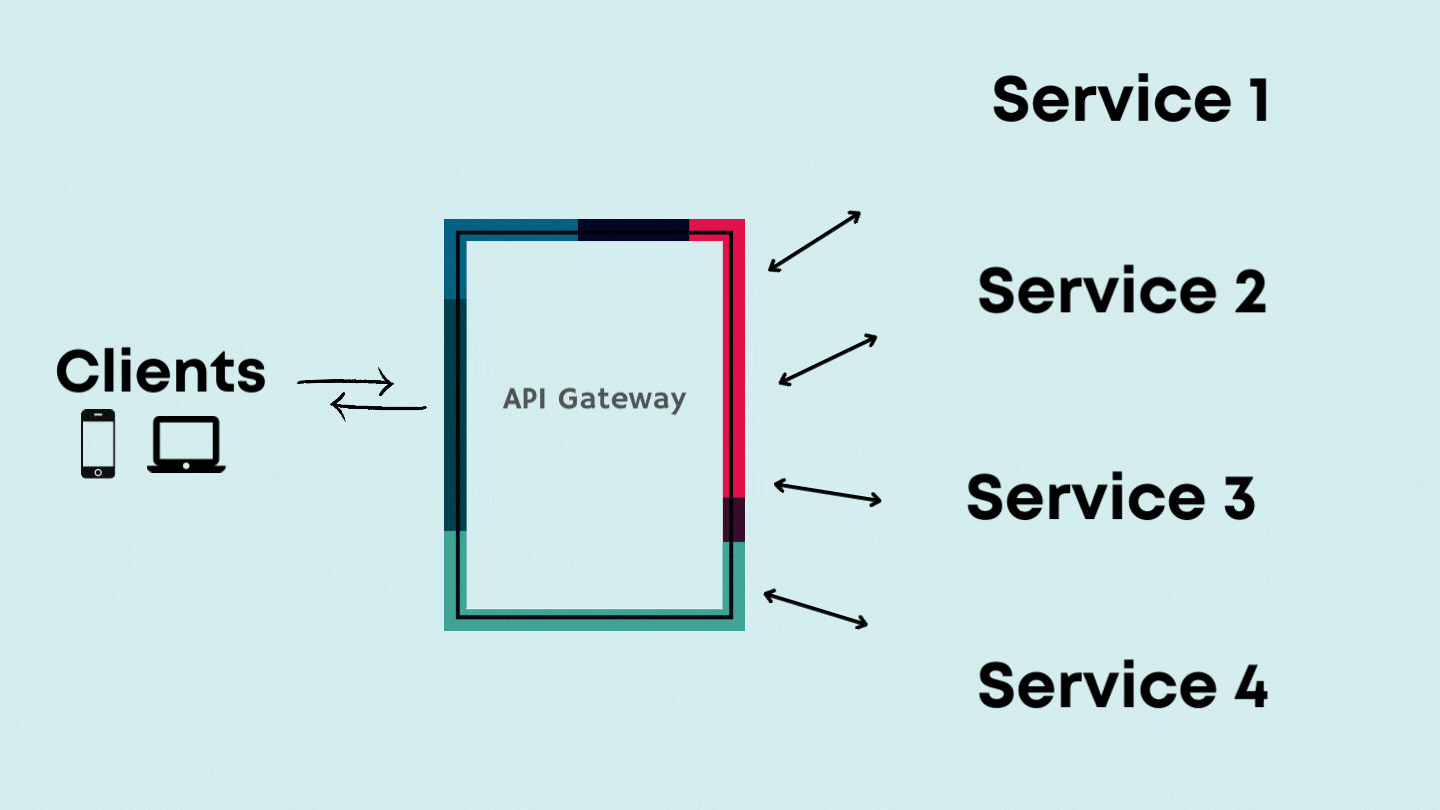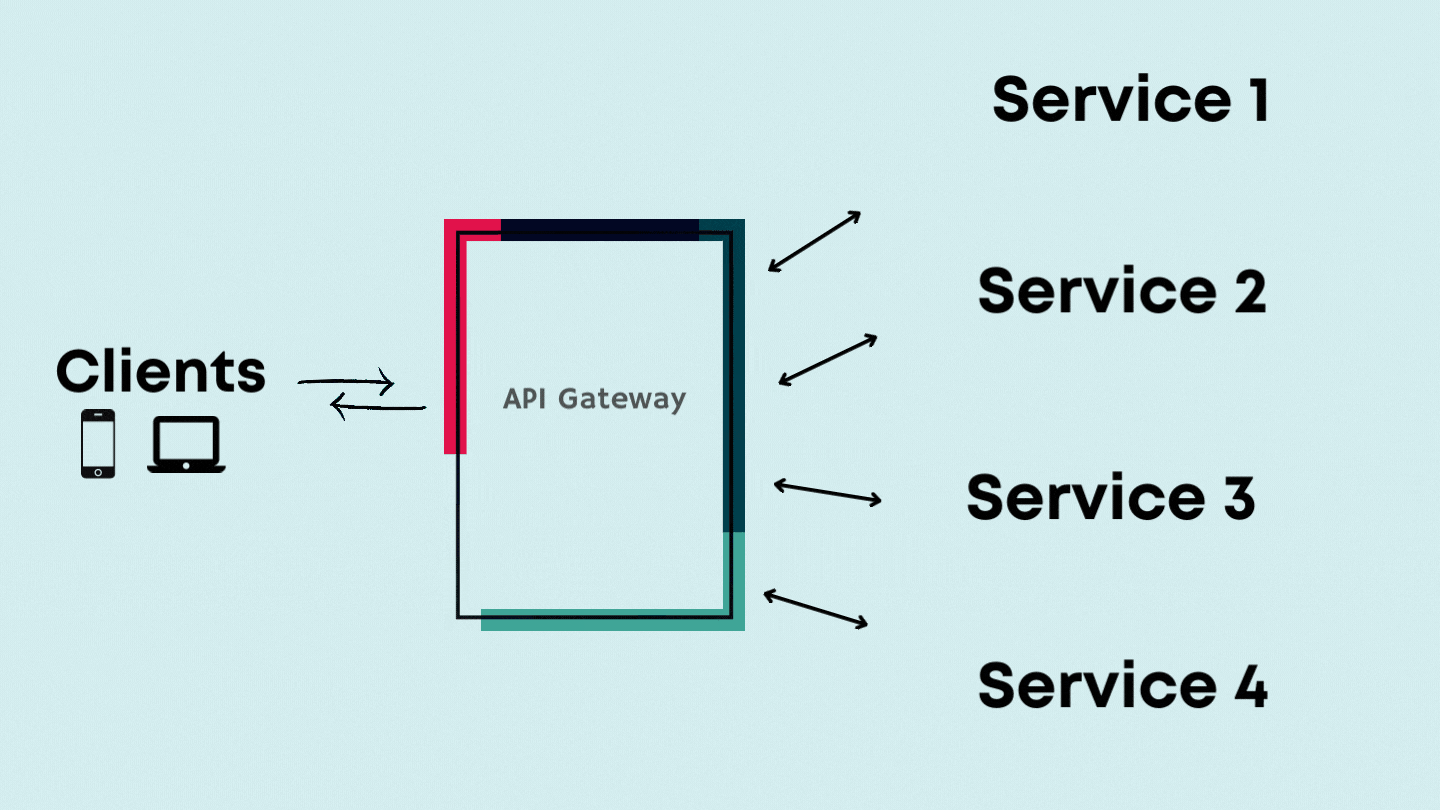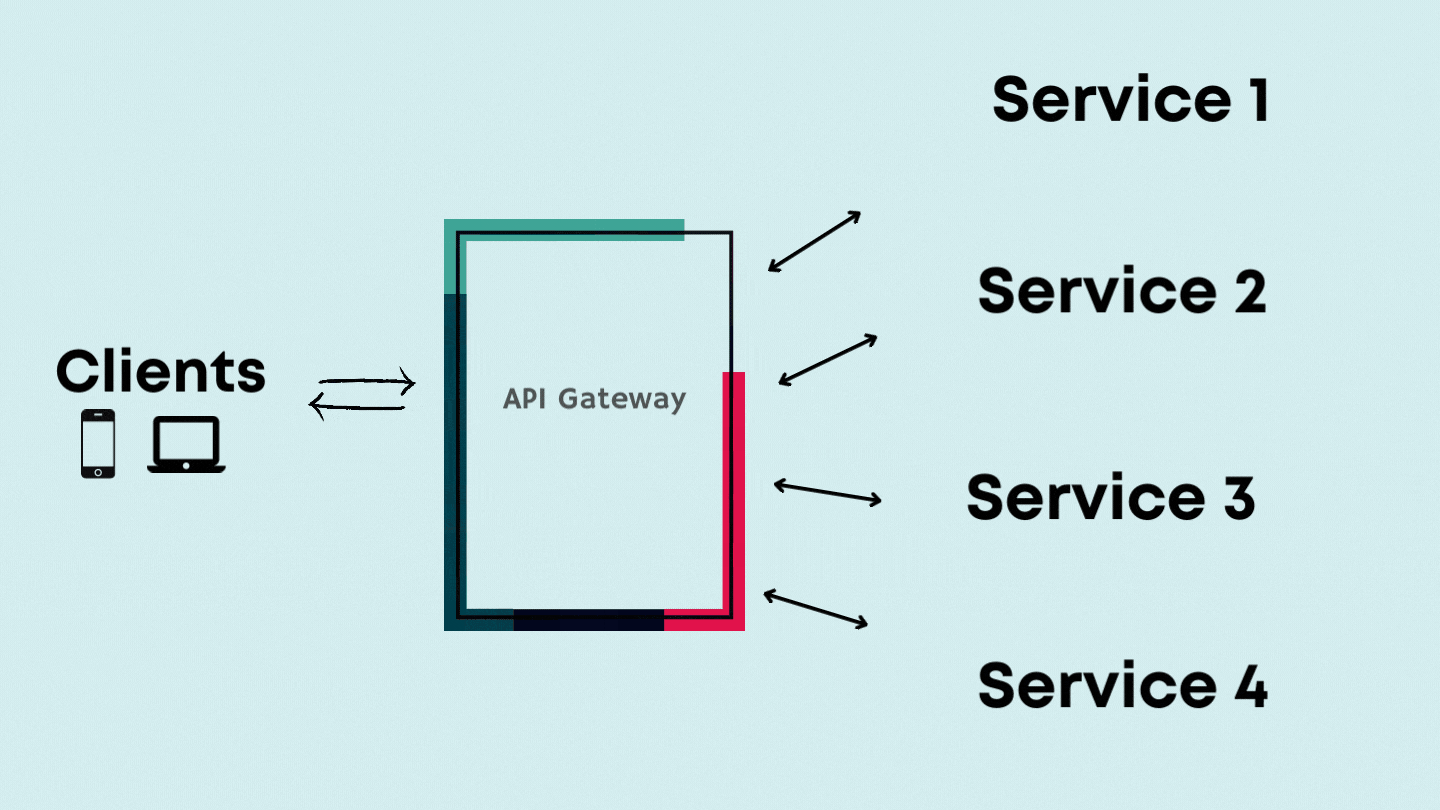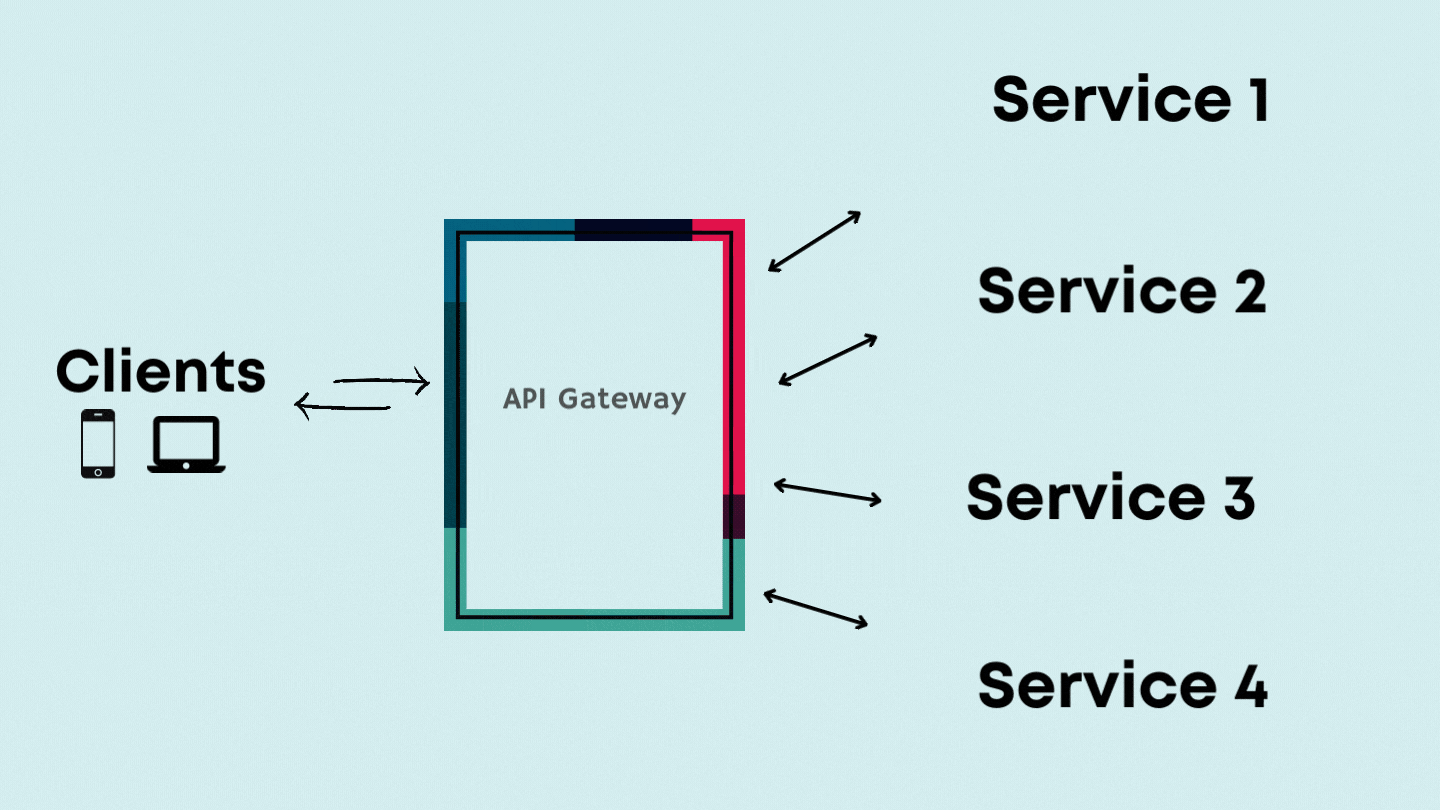
How does it work?
In the early 90’s, when the telephone was earlier introduced. Because of how new the technology was, connections between the callers and receivers were done manually. To manage the communication between clients, telephone companies set operators in charge of connecting the cables to callers and receivers. Think of API gateways as the operators. In a microservice architecture, communication between each microservice is done through APIs; a single API request by a client can prompt a response from numerous microservices. Subsequently, as the client's requests increase, communication will become too complicated to manage. So the API gateway sits between the client and the backend services as an operator for your API requests.
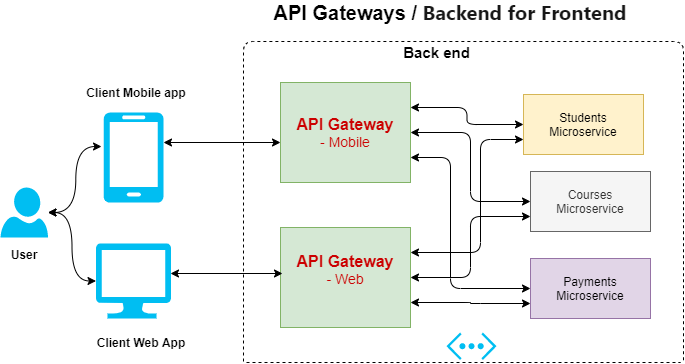
Every microservice within an application registers its details to the API gateways(name, location, port address etc.). Therefore, when a client maps an API call to a specific microservice, the API gateway acts as an orchestrator between various internal services. API gateways sit at the edge of your microservice architecture, providing a single entry point to your modern API enabled applications. Once an API request is made, a gateway will ensure it is in HTTPS using the SSL certificate. It then provides the user's authentication and authorisation to make these API requests. API gateways often handle other functions involved with APIs and microservices::
protocol translation
service discovery
basic business logic
authentication and security policy enforcements
stabilization and load balancing
cache management
monitoring, logging and analytics Features Of An API Gateway
Security
Features like SSL and authentication, and authorisation overcome security issues in a microservices architecture.
Reverse proxy or gateway routing API gateway provides a single endpoint or URL for the client apps and then internally maps the requests to a group of internal microservices. This decouples the client apps from the microservices. This is useful in modernising monolithic API for your application.
Authentication and authorisation Features like authentication and rate-limiting in API gateways help developers examine API abuse and overuse. They allow organizations to integrate and consolidate authentication providers for APIs using their protocol(s) of choice via API gateway.
API Traffic management & observability Multiple API handling is effortless with API gateway as ensure continual API performance. To achieve high availability for your applications and services, load balancing is combined with rate limiting and throttling. This protects the system from unexpected spikes in traffic or denial of service attacks.
Caching & CORS Policies Caching allows API platform to handle a higher number of clients. You can reduce the number of calls made to your endpoint and also improve the latency of requests to your API. Policies such as CORS(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) can also be enforced to allow the API to be accessed from a web browser.
Why Your Microservices Need An API Gateway
Create an Abstraction When developing a microservice application, numerous microservices get involved. A single request could require calls to dozens of different services, eventually bringing about complexities. Since the client cares more about a reliable and straightforward experience, API gateway is an abstraction between the client and the backend services decoupling requests. There is no need to bore the client with the details of the backend.
Orchestrates API gateways enable you to route based on path, hostname, headers, and other essential information carefully, avoiding any form errors.
Organise With real-time metrics and analytics, gateways help you troubleshoot problems faster and better understand the health of your microservices. Using the traffic throttle and API request authorisation features, API gateways permit backend developers to observe uninvited traffic spikes and ensure continual API performance.
Maintainability API gateways handle service discovery, API protocol translation, business logic processing, cache management, network traffic assistance, and API monitoring. It helps with getting every one of the required assets for API upgrade, redesigns, and modernisation, in any event, when updates are going on. API gateways are indispensable players in API management due to how they can handle API calls and disperse them to the concerned microservices.
Example of API Gateway
Apache APISIX is a cloud-native microservices API gateway, that delivers the ultimate performance, security, open-source and scalable platform for all your This text is a bit blunt, does it need to be interspersed with context? and microservices. Nginx and etcd are the foundations of Apache APISIX. Compared to your conventional API gateways, Apache APISIX provides traffic management features like Load Balancing, Dynamic Upstream, Canary Release, Circuit Breaking, Authentication, and Observability.
Conclusion and Takeaways
To conclude, integrations and interconnectivity between APIs with microservice architectures need to be carefully thought after. Think of an API gateway platform as an application server, but for APIs. Using API gateways, you can manage API traffic, monitor, and log all communication between microservices within your application. Features API Gateways provides help developers from manually building some of these services into monolithic and microservice applications.