When it comes to offering reliable and high-performance services worldwide, most communication systems encounter several cross-border problems. This article uncovers how HelloTalk overcomes these challenges, emerging as the world’s largest social foreign language learning platform using OpenResty and Apache APISIX.
What is HelloTalk?
HelloTalk is a language learning social platform that serves as a platform for diverse speakers of different cultures to teach and learn languages globally. There are over 160 languages that you can learn on HelloTalk. Some languages are: Arabic, Cantonese, English, French, Vietnamese, German, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Mandarin Chinese, Portuguese, Spanish, and more.
HelloTalk
Conversing, mistake correction and translation are all included in the program, and users may alter text by voice while chatting. HelloTalk supports voice to text and translation for over 100 languages. HelloTalk prioritizes both local and international communities of users by delivering high-quality services.
Users can learn other native languages and cultures with the community’s help. It is also a fantastic way to meet new people! HelloTalk has over 16 million users who are free to connect with learning partners for the language they wish to learn. Instead of conventional classes, users learn from a community of learners. Furthermore, users can also practice what they’ve learned on smartphones or tablets.
Challenges of Internationalization
- The HelloTalk users are widely spread. Therefore, It is necessary to find a solution to the problem of dispersed user distribution zones.
- Around 20% of HelloTalk customers in China are encountering firewall issues.
- The language environment in other nations is as complex as the network environment, making language adaptation a problematic task.
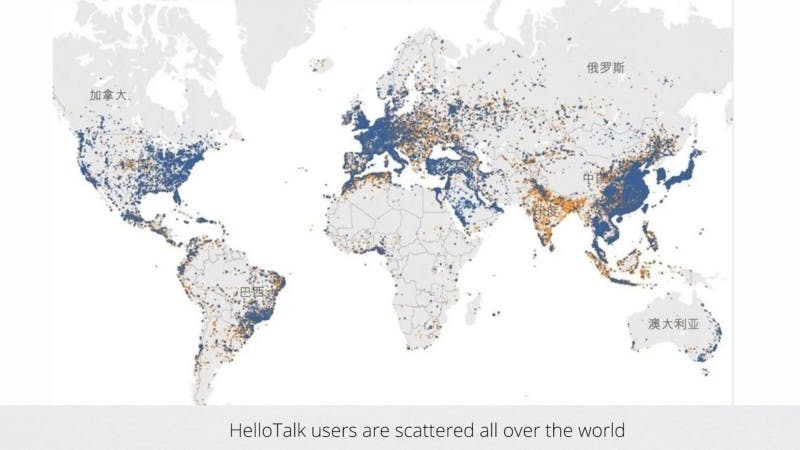
As illustrated in the diagram above, HelloTalk users are distributed worldwide. The distribution of HelloTalk users in Asia-Pacific, like South Korea, Japan, the Yangtze River Delta, and China’s Pearl River Delta, is significantly concentrated, making it easy to manage. However, delivering reliable service is difficult in other areas where customers are extensively dispersed, such as Europe, Africa, and the Middle East.
How To Improve User’s Global Access Quality
When thinking of improving the global user experience, HelloTalk considers two issues: cost and authentic quality of service. International customers are directly accelerated back to Alibaba in Hong Kong. Although direct acceleration risks degrading the client’s network quality due to geographical issues, HelloTalk implemented failover measures to improve user experience.
- Access Line Control and Traffic Management: The stability brought by the dedicated line network, such as Europe to Hong Kong, delay: 244 ms -> 150 ms;
- Dynamic upstream control (Lua-resty-healthcheck); flexible switching between several service provider lines is considered to ensure service reliability.
- Part of the logic can be processed directly at the edge, serverless (the principle is reliant on pcall + loadstring implementation), by transforming serverless into Apache APISIX + ETCD.
- Access Node and Quality Control
Due to how dispersed the access nodes of HelloTalk are, the United States can’t go directly to Hong Kong. Instead, the established mechanism only transfers to Germany before Hong Kong. So, to ensure that the user experience is not affected, Hellotalk considers specific failover measures to ensure that users can move between multiple service providers.
Choice of 7-layer and 4-layer Acceleration: Many service providers will provide 7-layer acceleration and 4-layer acceleration, but some problems need to be solved.
- Layer 4 acceleration: The SSL handshake time is too long and easy to fail, so it cannot obtain the client’s IP. Hence, making it inconvenient to the node quality statistics.
- Layer 7 acceleration: IM(Instance Message) services cannot guarantee the reliable arrival of messages that require a long connection
A management solution for global access in a multi-cloud environment:
- Layer 7 acceleration with support for WebSockets. (cloud service + self-built).
- Self-built low-speed VPC + dedicated line channel. (Considering the cost-effectiveness, IM itself does not have much traffic, so it only sends notification messages)
- Mixed sending and receiving messages with long and short connections: WebSocket + long polling + httpdns + built-in IP failover mechanism.
Why OpenResty?
OpenResty is a programming language that can create scalable online applications, web services, and dynamic web gateways. The OpenResty architecture is built on standard Nginx core and a variety of 3rd-party Nginx modules that have been enhanced to turn Nginx into a web app server capable of handling a vast number of requests.
HelloTalk’s IM services were once written in C++, and at that time, it used a high-performance network framework of a large manufacturing unit. Protocols were all drawn up internally, resulting in the seldom use of HTTP protocol; this didn’t seem cost-efficient for a smaller company.
Suppose the internal writing service is to be made available to the public. In that case, one must create a Proxy Server separately and the newly added command word adapted, which is time-consuming.
Hence, OpenResty was adopted to act as a proxy and directly convert the protocol to internal services. In the end, it reduced costs. The services were made available to the public, necessitating the use of WAF.
Previously, HelloTalk APIs were built using PHP; this left several loopholes due to framework issues resulting in countless cyber-attacks from hackers. The most common way was to post various PHP keywords or include PHP keys within URL characters.
HelloTalk tackled this challenge by adding tiny bits of code (based on regularisation) in OpenResty; it turned out that adding the WAF(Web application firewall) function did not affect performance loss.
Integrating OpenResty helped to tackle some of these challenges with the following benefits:
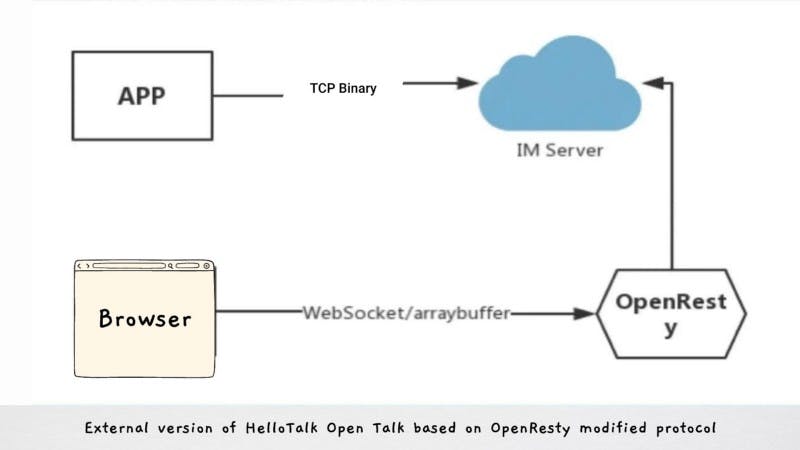
- Quickly implement a Web IM: Most mainstream IM(Instance Message) apps like WhatsApp and WeChat offer Web IM; hence the WebIM version of HelloTalk was implemented from the server-side based on OpenResty’s compatibility and modification of protocols. This was possible by simply adding a layer of OpenResty in the middle for WebSocket protocol conversion.
- By putting PHP function names in the WAF, all attempts of cyber attacks are blocked and unable to reach PHP.
- With openRestry, message limiting became possible, controlling the frequency of API calls/messages, which occurs directly based on resty.limit.req.
Integrating Apache APISIX
What is Apache APISIX
Apache APISIX is a dynamic, real-time, high-performance API gateway. It offers traffic management features such as load balancing, dynamic upstream, canary release, service meltdown, authentication, observability, and other rich traffic management features. It’s built atop the Nginx reverse proxy server and the key-value store etcd, to provide a lightweight gateway.
In the early days, to achieve dynamic modification for HelloTalk, Nginx.conf was altered directly to render the best performance, just as an API gateway would.
This proved a possible solution to achieving the high performance, dynamic update of SSL certificate, Location and upstream. Similar to the K8S ingress update mechanism, generated through a template: nginx_template.conf + JSON -> PHP -> Nginx.conf -> PHP -CLI -> Reload. The challenge with using this method was that many individuals forgot the priority order rules established by Location, often resulting in mistakes.
The adoption of Apache APISIX as the API gateway for HelloTalk reduced these challenges significantly with these benefits:
- APISIX is established on the Nginx library and etcd, saving the maintenance cost.
- The code is straightforward to comprehend, and it may understand regardless of skill set.
- It offers rich traffic management features such as load balancing, dynamic upstream, canary release, circuit breaking, authentication, observability, etc.
- It is an actively maintained project, and contributors/maintainers are prompt to render support via mailing lists.
- APISIX is relatively simple and easy to configure; although it is cumbersome, it does not rely on RDMS(Relational Database Management System), incurring additional maintenance costs.
- Apache APISIX is based on lua-protobuf. Hence, HelloTalk switched to using the lua-protobuf library, which can directly convert a PB object into JSON, making it convenient.
Conclusion
This post explains how HelloTalk previously devised alternative ways of achieving reliable and high-performance services globally. I also discussed the challenges with these configurations and the success story of adopting Apache APISIX and OpenResty.
Consider going through the docs for an in-depth understanding of Apache APISIX and its features.
You can find the original recording from HelloTalk on this topic here.

